Relays are fundamental components of modern electrical systems in today’s electrical world. A
Relay is essentially an electromechanical switch, where an electrical signal causes a mechanical contact to toggle between ON and OFF states. We use relays generously in automobiles, test and measurement equipment, power supplies, home automation systems, and many more. They are a very important part of an automotive electrical system, and hence it is very important to understand the Relay Wiring Diagram if you work on automobile electrical repair and maintenance.
So, in this guide, let us take a closer look at a typical automotive relay and the relay wiring diagram.
Outline
When working with relay wiring diagrams, it’s important to understand the symbols. Relay symbols may appear complicated at first, but they adhere to standard conventions that become easier to interpret with familiarity. Below are some commonly used symbols you may come across:
- Relay Coil: This symbol is typically a rectangle or a circle with a coil inside, representing the electromagnetic coil that activates the relay.
- Contacts: These symbols indicate the points where the relay connects or disconnects the circuit.
- Normally Open (NO): This contact remains open until the relay is activated.
- Normally Closed (NC): This contact remains closed until the relay is activated.
- Common (COM): This symbol represents the terminal that moves between the NO and NC contacts.
- Diode: Sometimes included in relay diagrams to protect against voltage spikes, depicted as a triangle with a line.
There are two types of commonly used automotive relays. They are:
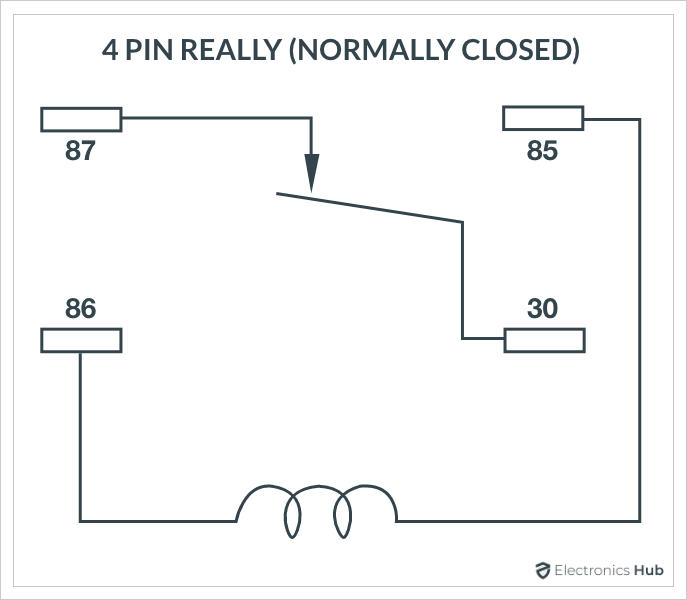
Normally Closed (NC) 4-Pin Relay.
Normally Open (NO) 4-Pin Relay.
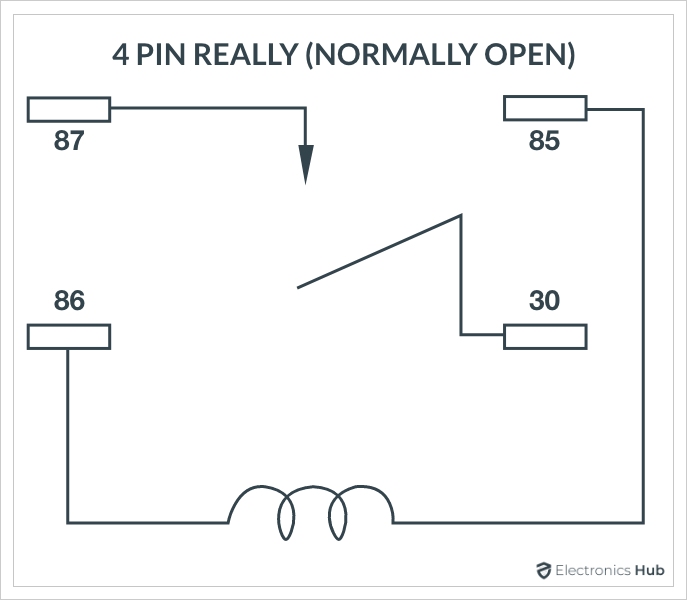
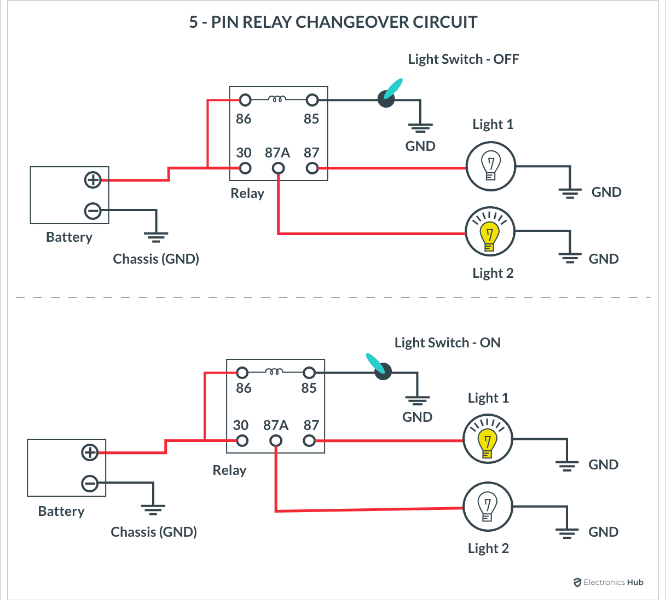
Both these relays are very similar except that the 4-Pin relay doesn’t have the ‘87a’ or the Normally Closed (NC) pin whereas the 5-Pin relay has it.
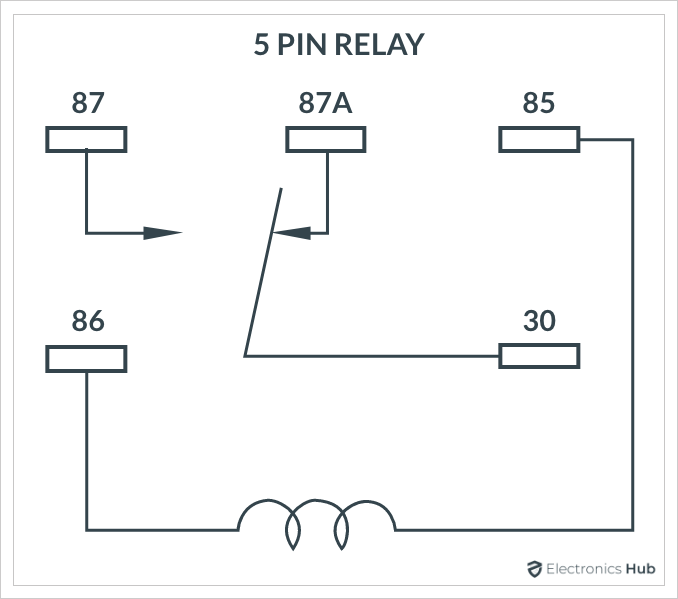
Another major
classification of automotive relays is the positioning of COM pin in the relay. Depending on position of the COM relays are further classified into:
- Type A Relay
- Type B Relay
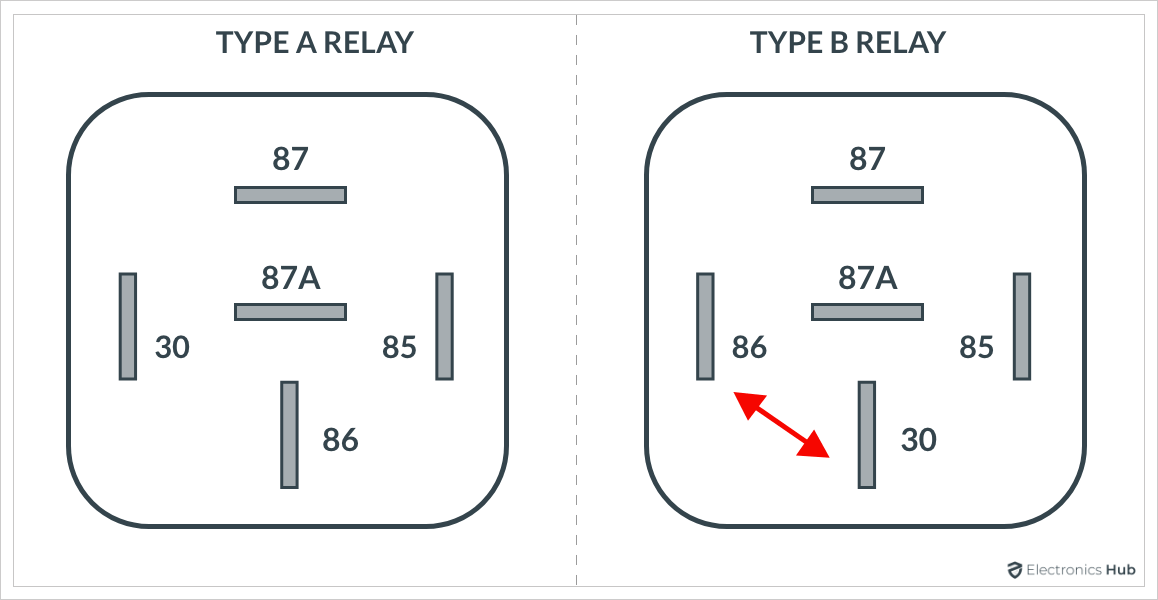
Th above image shows the difference between Type A and Type B relays. Note that these two types are available for both 4-Pin relays as well as 5-Pin relays.
Now that we have seen the important terminology associated with relays and also the pins, let us now take a look at some commonly used relay wiring diagrams.
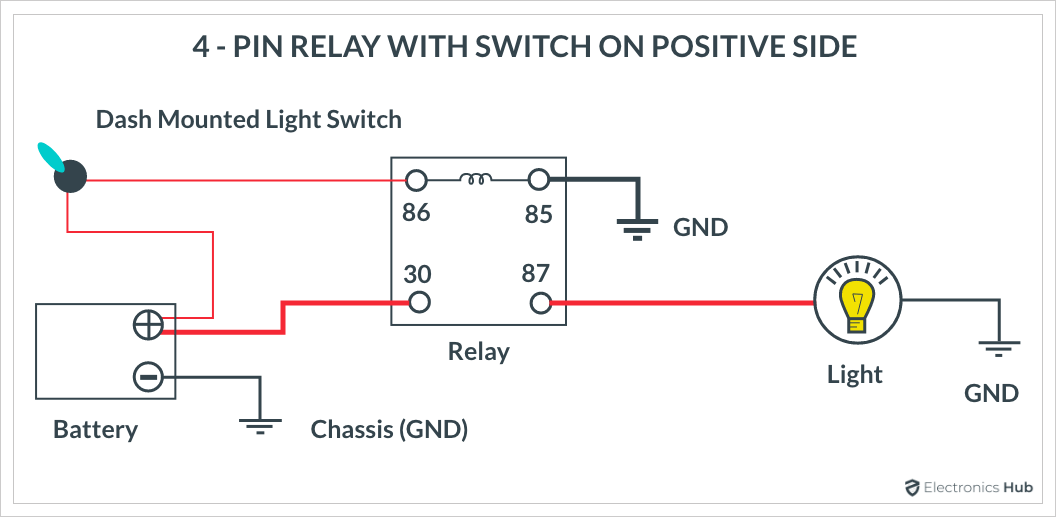
4-Pin Relay with Switch on Positive Side
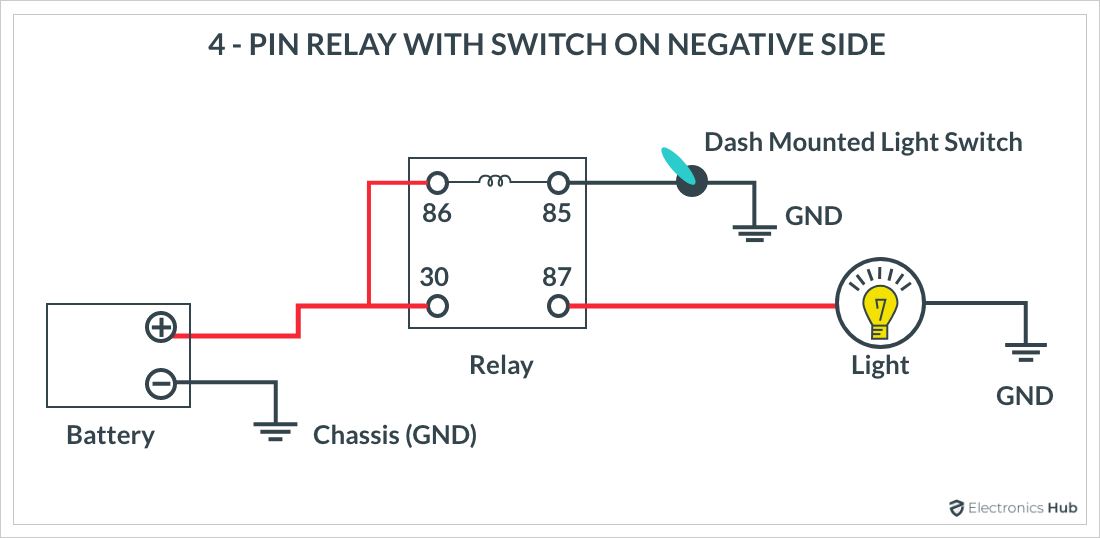
4-Pin Relay with Switch on Negative Side
5-Pin Relay to control two different circuits.
The beauty of relays is that the parts that acts as switch in the relay (which consists of the actuator and the contacts) are isolated from the mechanism that activates or deactivates the switch (which is the coil and electromagnet).
This construction is extremely useful if you want to control a large current switch with a tiny control signal from a microcontroller (or similar low voltage devices). This is exactly how we often use relays in real-life applications.
Assume there is a microcontroller which is configured to control an AC mains powered appliance. Relays are very useful in such scenarios as the microcontroller can provide the control signal to the relay’s coil and the contacts switch ON or OFF the appliance.
Another major application of relays is in automobiles. There are several high current/power components in a typical car (or any automobile for that matter) such as headlights, heater/cooling system, blower, motors, audio system, etc.
We can place the relays close to the appliance and send a tiny control signal wire from the car’s computer to the relay. This saves a ton of copper wire as the control wire doesn’t carry high current and all the high current devices are in the close proximity to the relay.
Reading and interpreting relay wiring diagrams involve understanding how these symbols interact within a circuit. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Relay Coil: Locate the relay coil symbol. This is where the control voltage is applied. The coil has two terminals, usually labeled 85 and 86. When voltage is applied across these terminals, it energizes the coil and activates the relay.
- Locate the Contacts: Find the NO, NC, and COM contacts. These will be labeled with numbers such as 30 (COM), 87 (NO), and 87a (NC for 5-pin relays). In a 4-pin relay, only the COM and NO contacts are used.
- Trace the Circuit Path: Follow the wiring diagram to see how the relay integrates into the circuit. Start from the power source and trace the path through the relay coil to understand how the control signal activates the relay. Then, follow the path from the COM terminal to the NO or NC contacts to see how the relay controls the load (e.g., lights, motor).
- Understand the Function: Determine the function of the relay in the circuit. For example, in a simple headlight circuit, when the relay coil is energized, the COM contact connects to the NO contact, allowing current to flow to the headlights.
- Check for Diodes: If a diode is included, ensure it’s placed correctly. The cathode (marked by a line) should connect to the positive voltage to protect against voltage spikes.
Consider a 4-pin relay used to control a car’s horn. The wiring diagram shows:
- Terminal 85 is connected to the ground.
- Terminal 86 is connected to the horn switch (which connects to the battery when pressed).
- Terminal 30 is connected to the battery.
- Terminal 87 is connected to the horn.
When the horn switch is pressed, voltage is applied across terminals 85 and 86, energizing the coil. This closes the circuit between terminals 30 and 87, allowing current to flow from the battery to the horn, thus sounding the horn.
1. What is the difference between a 4-pin and a 5-pin relay?
A 4-pin relay has two pins for the coil and two for the switching circuit (normally open), while a 5-pin relay includes an additional pin for a normally closed contact, allowing it to switch between two circuits.
2. How do I identify the pins on a relay diagram?
Relay pins are typically labeled as 85, 86, 30, 87, and 87a. Pins 85 and 86 control the coil, pin 30 is the common terminal, pin 87 is the normally open contact, and pin 87a (on 5-pin relays) is the normally closed contact.
3. Can I use a 5-pin relay in place of a 4-pin relay?
Yes, you can use a 5-pin relay in place of a 4-pin relay by simply not connecting the extra (87a) pin. However, ensure that the relay’s specifications match your application.
4. Why is a relay used in automotive wiring systems?
Relays are used to control high-current circuits with a low-current switch, protecting wiring and switches from damage and improving system efficiency.
5. What does a typical relay wiring diagram include?
A typical relay wiring diagram shows the coil connections, the switch terminals (normally open and/or closed), the power source, and the load. It may also include standard electrical symbols for easy interpretation.
Relays are very important part of many electrical system and they are an essential part of modern automotive ecosystem. They switch high power circuits with the help of isolated low power signals. Due to the mechanical nature of relays, they have wear-and-tear and we have to replace them in our cars and bikes. A knowledge of the pins of relays, relay terminology and also relay wiring diagram will be very useful if you are working with relays.